Polyvinyl Chloride – PVC
Polyvinyl Chloride, popularly known as PVC, is a high strength white, brittle solid thermoplastic that is lightweight, durable, low cost, and easy to process. PVC is the world’s third most widely produced synthetic polymer of plastic (after polyethylene and polypropylene).
PVC comes in two basic forms: rigid (sometimes abbreviated as RPVC) and flexible. The rigid form of PVC is used in construction for pipe and in profile applications such as doors and windows. It is also used in making plastic bottles, non-food packaging, food-covering sheets, and plastic cards (such as bank or membership cards). It can be made softer and more flexible by the addition of plasticizers, the most widely used being phthalates. In this form, it is also used in plumbing, electrical cable insulation, imitation leather, flooring, signage, phonograph records
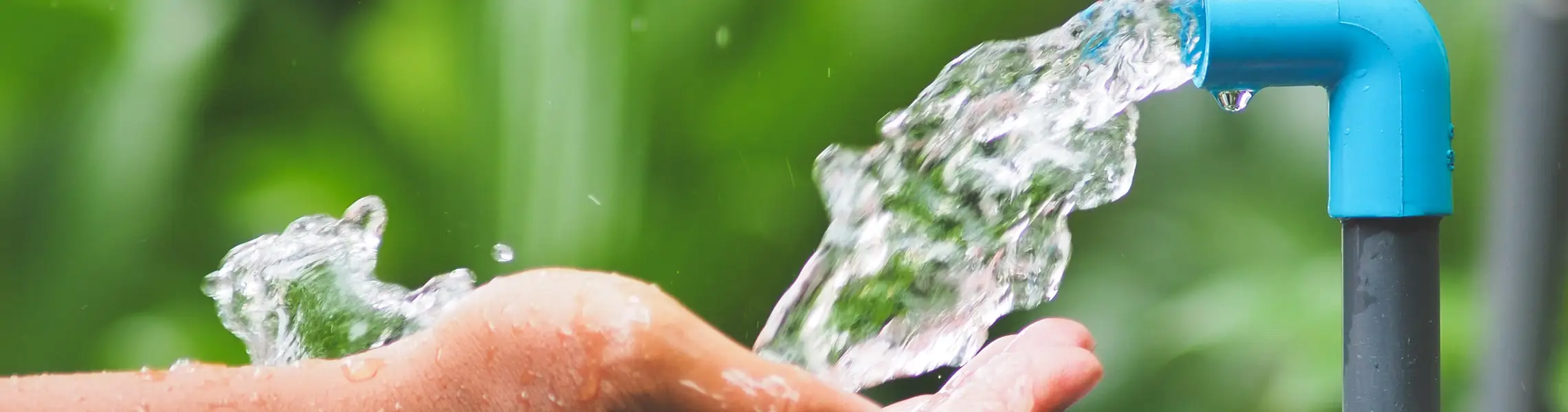
This means that this type of PVC does not contain any plasticizer, which is the solvent that is added to the PVC material to promote its plasticity, flexibility and reduce its brittleness. Since it does not contain this substance, PVC-U is often known as rigid PVC or RPVC. PVC used for pipes and fittings is utilized in the transportation of water, both drinking water and also wastewater. These types of pipes are easy to handle, light, affordable, durable, and because of the absence of a plasticizer in them, they are 100% recyclable.
When PVC undergoes this production process, unplasticized PVC is turned into a layered structure, which makes it more corrosion resistant. Its hydraulic capacity and durability are high, making it more suitable for pressure pipes for irrigation, drinking water, and sewer pumping mains.
Its characteristics are the same as PVC-U. It is manufactured for the transportation of drinking water and exhibits an excellent corrosion resistant property. The chlorination process of this type of polymer pipe differentiates because it is capable of withstanding a broader range of temperatures than other PVC. Due to this, C-PVC is mostly utilized in residential and commercial construction.
Benefits
dielectric strength, durability, flame resistant, low cost, abrasion and chemical resistance.
Applications
| Automotive & Electronic | Cables, interior door panels and pockets, instrument panels and associated moldings, Seat coverings, headlining, seals, mud flaps, sun visors, underbody coating, floor covering, exterior side molding, protective strips, anti-stone damage protection |
| Construction | Conservatories, window and door profiles, and atria, Pipes and fittings, power, telecoms, data wiring, and cables, cable and services ducting, ceiling systems, roofing, and membranes, soil, rainwater, and waste systems, flooring, wall coverings |